구조 패턴(Structural Pattern)
Composite 패턴은 객체지향 프로그래밍에서 사용되는 디자인 패턴 중 하나로, 여러 개의 객체들을 트리 구조로 구성하여 전체-부분 관계를 나타내는 패턴입니다.
이 패턴은 전체와 부분을 모두 같은 방법으로 다룰 수 있게 하며, 전체와 부분을 구분하지 않고도 동일한 인터페이스를 사용하여 다룰 수 있습니다. 이를 통해 전체와 부분의 계층 구조를 유지하면서, 각 객체들이 개별적으로 다루어질 수 있습니다.
Composite 패턴은 크게 Component, Leaf, Composite의 세 가지 클래스로 구성됩니다.
- Component : 전체와 부분을 모두 나타내는 인터페이스로, 전체와 부분을 동일한 방법으로 다룰 수 있도록 하는 역할을 합니다.
- Leaf : 부분을 나타내는 클래스로, 전체와 부분을 모두 다룰 필요가 없는 단일 객체입니다.
- Composite : 전체를 나타내는 클래스로, 하나 이상의 Leaf나 Composite를 포함할 수 있는 객체입니다.
Composite 패턴을 사용하면, 전체와 부분을 구분하지 않고도 일관된 방법으로 다룰 수 있어 코드의 유연성과 재사용성을 높일 수 있습니다. 또한, 객체의 계층 구조가 변경되어도 코드 수정이 적게 필요하다는 장점도 있습니다.
예를 들어, 파일 시스템을 모델링할 때 Composite 패턴을 사용할 수 있습니다. 디렉토리와 파일은 각각 Composite와 Leaf로 구분됩니다. 디렉토리는 다른 디렉토리와 파일을 포함할 수 있는 Composite이며, 파일은 부분을 포함하지 않는 Leaf입니다. 이렇게 모델링된 파일 시스템은 디렉토리와 파일을 동일한 방식으로 다룰 수 있으며, 유연하고 재사용 가능한 코드를 작성할 수 있습니다.
Composite 패턴 예제
Diagrams
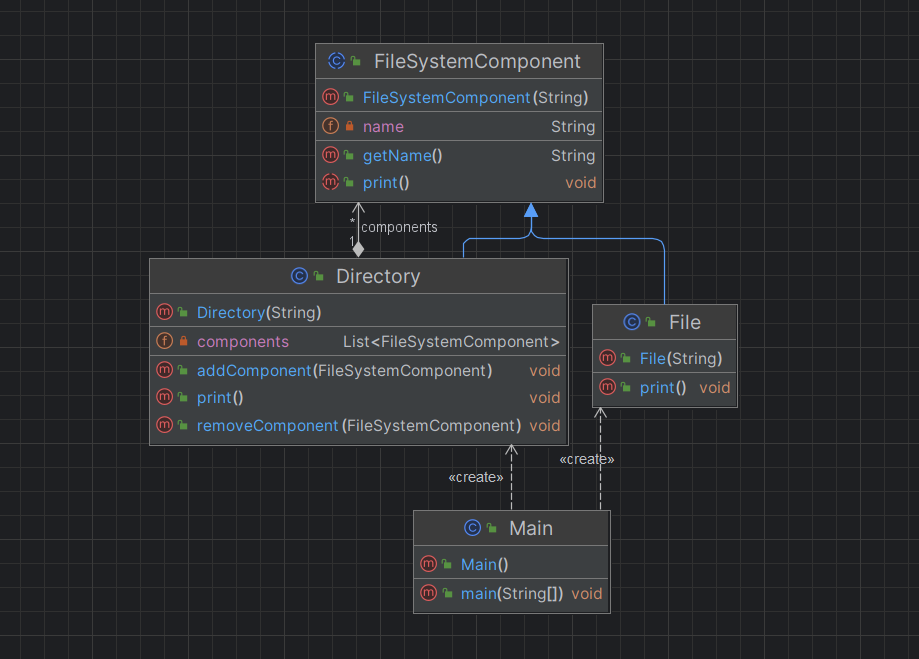
Component 클래스
public abstract class FileSystemComponent {
private String name;
public FileSystemComponent(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public abstract void print();
}
Leaf 클래스
public class File extends FileSystemComponent {
public File(String name) {
super(name);
}
public void print() {
System.out.println(getName());
}
}
Composite 클래스
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class Directory extends FileSystemComponent {
private List<FileSystemComponent> components;
public Directory(String name) {
super(name);
components = new ArrayList<FileSystemComponent>();
}
public void addComponent(FileSystemComponent component) {
components.add(component);
}
public void removeComponent(FileSystemComponent component) {
components.remove(component);
}
public void print() {
System.out.println(getName());
for (FileSystemComponent component : components) {
component.print();
}
}
}
이제 위에서 구현한 클래스들을 이용하여 파일 시스템을 만들어 보겠습니다.
public class FileSystemDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 루트 디렉토리 생성
Directory root = new Directory("Root");
// 디렉토리와 파일 생성
Directory dir1 = new Directory("Dir1");
Directory dir2 = new Directory("Dir2");
File file1 = new File("File1");
File file2 = new File("File2");
// 디렉토리에 파일과 하위 디렉토리 추가
dir1.addComponent(file1);
dir1.addComponent(dir2);
// 루트 디렉토리에 디렉토리와 파일 추가
root.addComponent(dir1);
root.addComponent(file2);
// 파일 시스템 출력
root.print();
}
}
위 코드를 실행하면 다음과 같은 출력이 나옵니다:
Root
Dir1
File1
Dir2
File2
이를 통해 Composite 패턴을 사용하여 파일 시스템을 모델링하고, 일관된 방식으로 다룰 수 있는 장점을 확인할 수 있습니다.
'JAVA > 디자인 패턴' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Design Pattern] Facade(퍼사드) 패턴이란? (0) | 2023.05.05 |
|---|---|
| [Design Pattern] Decorator(데코레이터) 패턴이란? (0) | 2023.05.02 |
| [Design Pattern] Bridge(브릿지) 패턴이란? (0) | 2023.04.30 |
| [Design Pattern] Adapter(어댑터) 패턴이란? (0) | 2023.04.30 |
| [Design Pattern] Singleton(싱글톤) 패턴이란? (0) | 2023.04.26 |



